- +91 9602036711
- +917357078560
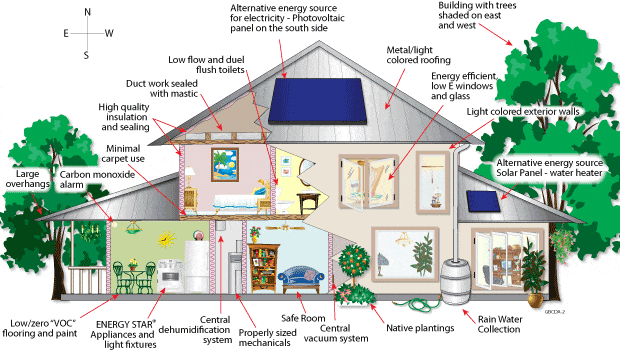
Green building, also known as sustainable or eco-friendly building, refers to the design, construction, and operation of buildings that prioritize environmental responsibility, energy efficiency, resource conservation, and occupant well-being. Green building practices aim to minimize the environmental impact of buildings throughout their lifecycle while creating healthier and more sustainable living and working spaces. Here are some key aspects of green building:

Energy Efficiency: Green buildings focus on reducing energy consumption through various strategies, such as using energy-efficient appliances and lighting, optimizing insulation, employing passive design techniques, and integrating renewable energy sources like solar panels.
Water Efficiency: Water conservation is another important aspect of green building. Strategies include installing low-flow fixtures, rainwater harvesting systems, gray water recycling, and efficient irrigation systems to minimize water usage and reduce strain on water resources.
Sustainable Materials: Green buildings prioritize the use of sustainable building materials, which are eco-friendly, non-toxic, and resource-efficient. These materials are often made from recycled or renewable sources and have minimal environmental impact throughout their lifecycle.
Indoor Environmental Quality: Green buildings focus on providing a healthy and comfortable indoor environment for occupants. This includes improving air quality, controlling humidity and temperature, maximizing natural daylight, and using low-emitting materials to minimize harmful emissions.
Waste Management: Green building practices incorporate waste reduction and recycling strategies. This involves designing buildings to generate less waste during construction and demolition, encouraging recycling and composting, and using recycled materials whenever possible.
Site Selection and Design: Green buildings consider the site’s environmental impact and aim to minimize disturbance to natural habitats and ecosystems. They may incorporate features like green roofs, rain gardens, and permeable pavements to reduce stormwater runoff and enhance biodiversity.
Lifecycle Assessment: Green building takes into account the entire lifecycle of a building, from construction to operation and eventual demolition. It aims to optimize energy and resource use, reduce environmental impact, and promote long-term sustainability.
Certification Systems: Various green building certification systems, such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method), provide guidelines and standards for evaluating and recognizing the sustainability of buildings.
By adopting green building practices, developers, architects, and occupants can contribute to mitigating climate change, conserving resources, improving indoor air quality, and creating healthier and more sustainable communities.
Green building materials, also known as sustainable or eco-friendly building materials, are materials that are used in construction and building processes to reduce the environmental impact of buildings. These materials are designed to be energy-efficient, non-toxic, durable, and made from renewable or recycled sources. Here are some examples of commonly used green building materials:
Bamboo: Bamboo is a rapidly renewable resource that can be used as an alternative to traditional wood. It is strong, lightweight, and versatile, making it suitable for various applications such as flooring, furniture, and structural elements.
Recycled Steel: Using recycled steel in construction helps reduce energy consumption and lowers the demand for new steel production. Recycled steel is commonly used for structural support, roofing, and framing.
Fly Ash Concrete: Fly ash is a waste product from coal-fired power plants. When mixed with cement, it can replace a portion of the cement content in concrete, reducing the need for new cement production and lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
Recycled Plastic Lumber: Made from recycled plastic, this material is an eco-friendly alternative to traditional wood lumber. It is commonly used for decks, outdoor furniture, and landscaping.
Insulated Concrete Forms (ICFs): ICFs are blocks or panels made from materials such as expanded polystyrene (EPS) or recycled wood fibers. They are used to create insulated walls that provide better energy efficiency and thermal performance.
Cork: Cork is a renewable resource obtained from the bark of cork oak trees. It is commonly used as flooring material due to its durability, thermal and acoustic insulation properties, and sustainability.
Low VOC Paints: Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are chemicals found in many conventional paints that can have harmful effects on indoor air quality. Low VOC or zero VOC paints have reduced levels of these harmful chemicals, making them better for human health and the environment.
Solar Panels: While not a building material per se, solar panels are often integrated into sustainable building designs to generate renewable energy and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
These are just a few examples of the many green building materials available. Sustainable construction practices and the use of such materials can contribute to energy efficiency, reduced waste generation, and improved environmental performance in the construction industry.
What Are The Components Of Green Building
Green building incorporates various components and strategies to achieve sustainability and reduce environmental impact. Here are some key components of green building:
Energy Efficiency: Energy efficiency is a crucial component of green building. It involves designing and implementing measures to minimize energy consumption, such as using energy-efficient appliances, incorporating insulation, optimizing HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems, and utilizing natural lighting and ventilation techniques. The goal is to reduce the building’s reliance on fossil fuels and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Water Conservation: Water conservation focuses on reducing water usage and promoting efficient water management. This includes implementing water-saving fixtures, such as low-flow toilets and faucets, utilizing rainwater harvesting systems, employing gray water recycling for non-potable uses, and designing landscape irrigation systems that minimize water waste.
Sustainable Materials: The use of sustainable materials is essential in green building. This involves selecting materials that are environmentally friendly, energy-efficient, and made from renewable or recycled sources. Examples include bamboo, recycled steel, reclaimed wood, recycled plastic, and low VOC (Volatile Organic Compound) products. The aim is to reduce resource depletion and minimize waste generation.
Indoor Environmental Quality (IEQ): Green building emphasizes creating a healthy and comfortable indoor environment for occupants. This involves incorporating measures to improve air quality by using proper ventilation systems, selecting low-emitting materials, managing moisture and humidity levels, and promoting access to natural daylight. Enhancing indoor environmental quality contributes to occupant well-being and productivity.
Site and Location: The site and location of a building play a significant role in green building. Factors to consider include selecting sites with minimal environmental impact, proximity to public transportation, walkability, and access to amenities. Green building also encourages preserving natural habitats, reducing light pollution, and implementing stormwater management strategies.
Waste Management: Green building promotes waste reduction and efficient waste management practices. This includes minimizing construction and demolition waste through recycling and reuse, incorporating waste separation systems within buildings, and considering strategies for ongoing waste management during the building’s operation.
Renewable Energy: Integration of renewable energy sources is a key component of green building. This involves incorporating technologies such as solar panels, wind turbines, or geothermal systems to generate clean and sustainable energy for the building’s operation. Utilizing renewable energy helps reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lowers carbon emissions.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA): Green building considers the entire life cycle of a building, including construction, operation, maintenance, and eventual demolition. Life cycle assessment evaluates the environmental impact of materials, systems, and design choices, enabling informed decision-making to minimize the overall environmental footprint.
These components work together to create sustainable and environmentally responsible buildings that minimize energy consumption, conserve water, promote occupant health and well-being, reduce waste, and utilize renewable resources. Green building practices contribute to a more sustainable built environment and help mitigate the environmental impacts of the construction industry.
What type of plastic is used in Building Construction
In building construction, several types of plastics are commonly used for various applications. Here are some of the plastics commonly used in the construction industry:
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): PVC is a widely used plastic in construction. It is commonly used for pipes, fittings, and plumbing systems due to its durability, chemical resistance, and low cost. PVC is also used for window frames, flooring, roofing membranes, and electrical insulation.
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE): HDPE is a versatile plastic with excellent strength and chemical resistance. It is used for applications such as water and gas pipes, drainage systems, geomembranes, and plastic lumber. HDPE is also used in underground electrical conduits and protective barriers.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): ABS is a rigid thermoplastic used in construction for pipes, fittings, and drain-waste-vent (DWV) systems. It is known for its high impact resistance and can be easily bonded using solvents.
Polycarbonate (PC): Polycarbonate is a transparent and impact-resistant plastic that is commonly used for glazing applications. It is used in the construction of skylights, roofing panels, safety windows, and sound barriers.
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET): PET is a commonly used plastic in construction for applications such as insulation, carpet fibers, and acoustic panels. It is also used in the production of bottles and packaging materials.
Polypropylene (PP): Polypropylene is a lightweight plastic with good chemical resistance. It is used in construction for applications such as pipes, fittings, thermal insulation, and waterproofing membranes.
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS): EPS is a lightweight and rigid plastic foam used as insulation material in building construction. It is commonly used in the form of foam boards or as part of insulated concrete forms (ICFs).
Polyurethane (PUR): Polyurethane is a versatile plastic used in building construction for insulation panels, sealants, adhesives, and coatings. It provides excellent thermal insulation and is commonly used in spray foam insulation.
It’s important to note that while plastics offer advantages in construction, their environmental impact and sustainability should be considered. Increasingly, there is a focus on reducing plastic waste, promoting recycling, and exploring alternative materials to minimize the ecological footprint of the construction industry.
What plastics are removed in green building construction
In green building construction, efforts are made to reduce the use of certain plastics that have a higher environmental impact or are less sustainable. Here are some examples of plastics that are often minimized or avoided in green building practices:
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): PVC, although widely used in construction, can pose environmental and health concerns due to the presence of additives like phthalates and chlorine. In green building, there is a preference for alternative materials or low-impact alternatives to PVC, particularly for applications like flooring, pipes, and window frames.
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) Foam: While EPS foam is commonly used for insulation in construction, it is not considered highly sustainable due to its limited recyclability and potential for environmental pollution. In green building, there is a shift towards using alternative insulation materials with lower environmental impact, such as natural fibers, cellulose insulation, or recycled materials like cotton or denim insulation.
Single-Use Plastics: Green building practices aim to reduce the use of single-use plastics, such as plastic packaging materials, disposable containers, and plastic bags. Efforts are made to promote reusable or recyclable alternatives and minimize waste generation.
Non-Recyclable or Difficult-to-Recycle Plastics: Plastics that are not easily recyclable or have limited recycling infrastructure may be avoided in green building. This includes certain types of plastic films, laminates, and composites. Instead, materials that have better recyclability or sustainable alternatives are preferred.
High-Impact or Low-Durability Plastics: Plastics that have a high environmental impact in their production or disposal, or those that have low durability and require frequent replacement, are minimized in green building. This includes plastics that may be prone to degradation, brittleness, or UV damage, leading to shorter lifespans. Instead, more durable and long-lasting materials may be chosen.
It’s important to note that the focus of green building is not solely on avoiding plastics but on adopting a holistic approach that considers multiple environmental and sustainability factors. This includes energy efficiency, water conservation, resource efficiency, indoor air quality, and the use of environmentally friendly materials throughout the building’s lifecycle.